If you’re new to the world of crypto and want to understand how blockchains work, it may be a good idea to start with protocols. Protocols are the backbone of the crypto ecosystem. They are what make each unique feature of crypto possible.
What is a protocol?
In everyday language, “protocol” means a set of rules. The term has a similar meaning in the world of technology and crypto. But it refers to something a little more specific here. In crypto or any other information technology system, protocols are the rules that govern data sharing between computer systems.
These protocols are basically rules that help define how users send and receive information on the network. They do this to secure information transfers and to ensure that the intended recipients do in fact receive the information.
All applications are built on a foundation of protocols.
Some of the more well-known internet protocols come with the https tag (those letters found before any website address), DNS, TCP/IP, and VoIP.
Protocols in blockchains
A blockchain consists of computers from across the globe working in sync and forming a network. The protocols in blockchains are what help the computers coordinate. Each device, therefore, works independently but in accordance with the protocols of the underlying blockchain system.
If any device malfunctions or processes information wrongly, the protocol identifies it and kicks it out. In this way, it keeps the system immutable.
To sum it up, the protocol of a blockchain does the following:
- Processes transactions;
- Serves as a mechanism that oversees and governs all participating nodes as they interact with each other; and
- Creates an application programming interface.
Let’s take the example of Bitcoin. Each node (computer) in the network works on rules that all participating nodes have agreed upon in advance. Every one of them is competing to verify transactions and add them to the blockchain as per the pre-defined rules or protocols. The protocols are meant to enable peer-to-peer transactions.
Also, all nodes always store an updated copy of the blockchain’s transaction records. Therefore, if any node wants to change a record, the protocol mandates that it can only do so by also changing the records of all the nodes. Since it is impossible to tamper with the network ledger (at least not without informing everyone else), the protocol is at the heart of Bitcoin’s model of network security.
What is the difference between blockchain and protocol?
The terms “blockchains” and “protocol” do not mean the same thing. Technically speaking, they are two very different concepts.
A protocol forms the foundation of the blockchain platform. It is the foundational layer of code that sets up the framework for all activity on the blockchain. Protocols determine the storage and transaction verification processes of digital assets. They level the playing field for all nodes of the blockchain network.
Blockchain networks, on the other hand, are the ledgers that protocols help create and run.
A protocol can support multiple blockchains. The teams that develop protocols often end up going down separate paths in the future but can and do create their own blockchain networks on the same protocol. That’s how one protocol ends up supporting multiple networks.
What are thin protocols and fat protocols?
The concepts of thin and fat protocols were introduced by Joel Monegro in 2016. They help us improve our understanding of the difference between Web 2.0-based applications and blockchain-based ecosystems.
The web, as we know it today, is said to have a “thin protocol layer.” That means the value (market capitalization) in Web 2.0 is usually based on the upper application layer, largely in the form of data. The thinness of this protocol layer has to do with the fact that investment in the Web 2.0 application layer generates more profits than protocol technologies.
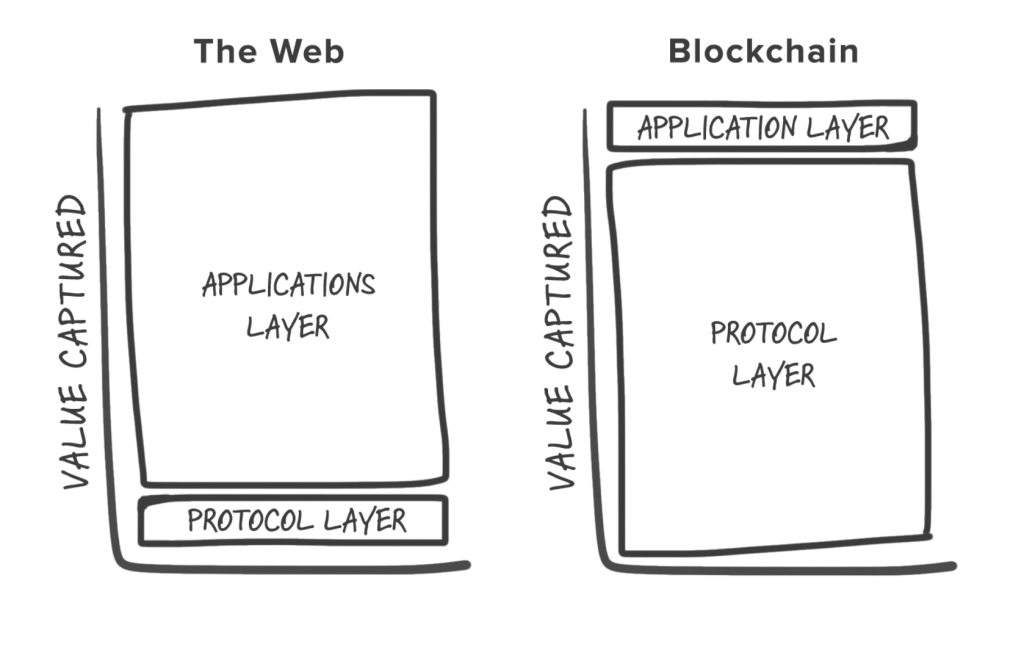
A representation of fat and thin protocol layers
Source: USV Investment Thesis
The arrival of blockchain-based applications reversed this. The protocol layer of blockchains is “fat” because that’s where the bulk of its value lies. Only a small fraction of data stems from the application layer. For instance, the value of two of the world’s leading blockchains, Bitcoin and Ethereum, relies on the utility of their protocols, not the applications built on top of their blockchains.
With blockchains, the applications on top of their fat protocols also help create value for protocol tokens. The resulting higher value of tokens in turn attracts new participants, miners, stakers, users, and investors. The more successful the applications are, the higher the value of fat protocols.
Why are protocols important?
With the evolution of digital systems, protocols allow connected devices to communicate with each other, enabling the exchange of data and services. That means it helps them overcome any differences in internal processes, structure, and design. Therefore, protocols are a fundamental part of digital communication.
Protocols are important in the digital world because they perform the following functions.
- Data sequencing: They help with the sorting of data within a specific time frame. That involves the inclusion as well as the exclusion of information.
- Data flow: They primarily deal with sending data to the correct address. In that sense, they check whether the flow of data is correct.
- Data routing: Protocols help determine the best possible path for data flow between the sender and the receiver.
- Encapsulation: They implement and manage the process of data transfer. The process is called encapsulation.
- Connection control: The connection-oriented data transfer for lengthy data items is ensured by protocols.
- Transmission services: The primary role of protocols is to deal with priority, quality of service (QoS), and security of data packets at every stage of transmission and storage.
- Flow control: Protocols are also responsible for limiting data flow. They also ensure that the receiver’s end maintains flow control.
- Error control: The detection of errors in the transmission, storage of data during data flow, and sequencing are all functions of protocols. Additionally, they are also responsible for discarding corrupt data packets.
Some of the essential features of blockchain protocols should help further your appreciation of protocols. The key features are:
- Decentralization: Information stored in blockchain protocols must be stored in a decentralized manner that can be accessed, copied, and viewed by any node in the network. The protocol makes this possible.
- Immutability: Protocols play a key role in ensuring that all records are permanent and cannot be changed.
- Consensus-drivenness: The data or transactions recorded on the blockchain must be verified and added only after all participating nodes arrive at a consensus. Protocols look into this too.
Conclusion
As more and more parts of the world take the decentralized route, developers will have to strengthen their blockchain protocol game. Strong protocols are the key to a crypto’s sustainable development. That’s why two of the world’s largest blockchains, Bitcoin and Ethereum, have undergone updates to make their protocols stronger. Doing so also creates value for holders and drives innovation.
If you are looking to invest in a crypto token, your first step should be to understand how strong the underlying protocol is. A high adoption rate among developers is a good sign.
FAQs
What are the key components of a blockchain protocol?
Consensus, cryptographic hashing, distributed ledger, smart contracts, and peer-to-peer network are key components of a blockchain protocol.
How does a blockchain protocol enable secure transactions?
Blockchain protocol uses cryptographic techniques to verify and link transactions in blocks, making it difficult to alter past data, ensuring security.
What are the benefits of using blockchain protocols?
Decentralization, transparency, immutability, enhanced security, reduced fraud, faster and more efficient transactions, and improved supply chain management are blockchain protocol benefits.








