The annual ritual that unfolds with clockwork precision is boringly familiar: The months-long run-up to the D-Day, the finance minister distributing halwa to staff, officials staying back in the North Block to ensure utmost secrecy, and the customary photo on the steps of the Parliament House. Yet, what remains under wraps is the content of the national budget to be presented on 1 February, which has everyone glued to their TV sets and phones, curious to know what is in it for the aam janta and India Inc.
Truth be told, the Union Budget of India is more than just an estimate of income and expenditure for the upcoming financial year. Read on as we fill you in on everything you need to know about the budget: its definition, significance, and the key terms used.
What is the Union Budget?
According to Article 112 of the Indian Constitution, the Union Budget is the annual financial statement that details the estimated receipts and expenditures of the government of India for the financial year that runs from 1 April to 31 March. The national budget is presented in both houses of Parliament.
The receipts include revenue from direct and indirect tax collections, disinvestment, and dividend collection.
The finance ministry, in consultation with stakeholders, prepares an estimated expenditure estimate for developmental work in various sectors of the economy such as agriculture, education, industry, infrastructure, health, transport, and manufacturing.
The budget session of Parliament begins with the tabling of the Economic Survey in both houses of Parliament a day before the presentation of the Union Budget. The Chief Economic Adviser (CEA) supervises the preparation of The Economic Survey, which documents the state of the economy.
While presenting the Union Budget is an annual ritual, the Finance minister presents a Interim Budget in the year in which elections are due.
What is an Interim Budget?
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman will present the Interim Budget for the financial year 2024-25 in Parliament on February 1. We all know that a budget is a statement of the government’s revenue and expenditure. The Interim Budget, as the term indicates, is a temporary arrangement before a full Budget can be presented. Essentially, an Interim Budget is presented by the incumbent government when it is going through a transition period or is in its last year in office ahead of the general elections. A copy of the Interim Budget is laid in the Rajya Sabha after it is presented in the Lok Sabha.
In an Interim Budget, also called the Vote on Account, the ruling government seeks a vote of approval from Parliament to draw money from the Consolidated Fund of India to carry on work for the time being until a new government is sworn in.
The full Union Budget will be presented by the newly-elected government after the Lok Sabha polls scheduled to be held in April/May.
What is included in the Interim Budget?
The Interim Budget is presented by the government to account for a short period of three to four months. Typically, the budget document will outline the government’s economic vision for the next five years, should it return to power. The Interim Budget also sums up the government’s record in raising revenue and containing expenditures as proposed in last year’s budget.
What is not included in the Interim Budget?
Usually, the incumbent government does not announce major policy changes in the Interim Budget. According to the Election Commission’s Code of Conduct, the ruling government cannot launch any major scheme in the Interim Budget ahead of the elections as it could influence voters.
Parliamentary convention suggests that the government in power is not expected to present the Economic Survey before the Interim Budget in an election year. The Economic Survey will be presented the day before a full Budget is presented by the newly elected government.
Types of Union Budget
The Union Budget is broadly divided into revenue and capital budgets.
Revenue budget
Put simply, the revenue budget documents the revenue the government receives through taxes and other sources and mentions how these are spent. Expenditures can range from day-to-day expenses incurred for the functioning of the government and for implementing schemes for the welfare of citizens and other services.
Capital budget
The capital budget keeps tabs on capital receipts and payments. If there is a shortfall in expected tax revenue collection, the government takes the money market or debt route to fund the shortfall. Government capital receipts come from loans from the public/market, RBI, and other financial institutions like the IMF, World Bank, or even foreign governments. Capital payment is the amount that is paid for servicing capital receipts or loans. For example, the repayment of interest or principal to the bondholder on maturity.
A budget is a financial statement that presents estimated government expenditures and receipts or revenues expected for the upcoming financial year. Based on the practical applicability of these projections, budgets fall into three broad buckets—-balanced budget, surplus budget, and deficit budget.
Balanced budget: In a balanced budget, total expected revenues and planned expenditures are equal. However, such a budget is rare, practically speaking.
Surplus budget: In a surplus budget, government receipts exceed expenditures. A surplus budget is not ideal for any economy as it indicates inefficient use of resources by the government.
Deficit budget: When the planned spending outpaces the total estimated revenue receipts, it is a deficit budget. India has a deficit budget. In fact, a healthy deficit shows the government’s resolve to spur growth through higher spending and create more employment opportunities.
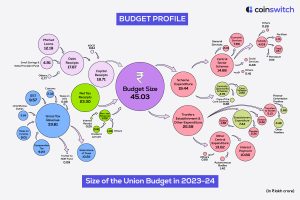
Importance of the Union Budget in India
The Union Budget, also termed the general budget, is a deft balancing of revenue and capital budgets. It contains the details of the expenditures to be allocated to different sectors of the economy to stimulate growth. Through these allocations, the budget aims to generate meaningful employment opportunities. The budget solely focuses on addressing the challenges the economy is currently facing and achieving developmental targets.
The Union Budget mainly seeks to achieve five primary objectives:
- Ensure efficient allocation of resources in the best interests of the economy and achieve maximum value for every rupee spent on social welfare schemes.
- Controlling prices and keeping the economy stable. Include provisions in the budget to handle inflationary and deflationary pressures.
- Reducing wealth and income disparities through changes in tax structures and subsidies
- Reducing poverty through targeted social security schemes and creating more job opportunities
- Implement changes in tax structure to improve tax collections and widen the taxpayer base
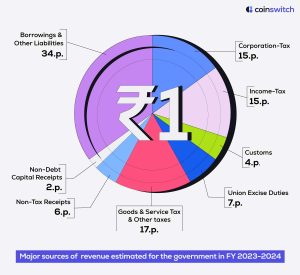
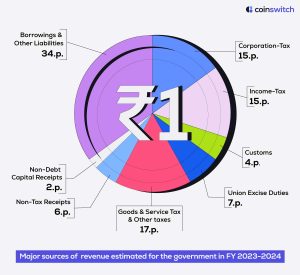
How did the government finance its revenue deficit in 2023-2024?
- Market borrowings (G-secs and T-bills)
- Security against small savings
- State provident funds
- Internal debt and public accounts
- External Debt
What is the difference between revenue deficit and fiscal deficit?
Revenue deficit refers to the excess of revenue expenditure over receipts. Fiscal deficit refers to the excess of total government expenditure over total tax and non-tax receipts, excluding debt.
Fiscal deficit indicates how much the government needs to borrow from the market and other sources to meet expenditures. Depending on the quantum of fiscal deficit, the government plans the disinvestment targets and market borrowings.
Often, the government fails to keep the fiscal deficit target under check or exceeds it during the financial year. It indicates inefficiency in government functioning. Further, it can lead to inflationary pressures, low GDP growth, and even a debt trap. Worse, it erodes the nation’s credibility in the domestic and international markets and hurts investments.
How does the Union Budget process end?
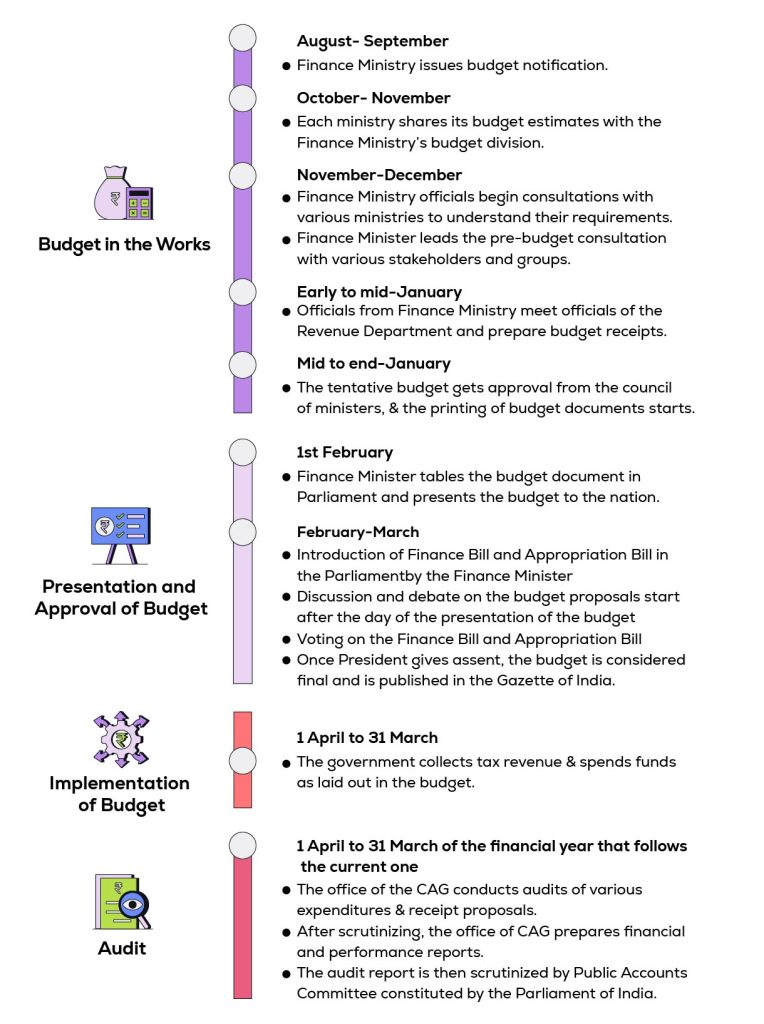
Usually, a general discussion in both houses of Parliament follows the presentation of the budget, typically the day after. The discussion evaluates the proposals outlined in the budget and the government’s fiscal policy. Following deliberations, including the Demands for Grants, the lower house (Lok Sabha) passes the Appropriation Bill and authorizes the government to spend money from Consolidated Funds of India.
After the Appropriation Bill and Finance Bill are passed by the lower house, it goes to Rajya Sabha, the upper house. Rajya Sabha does not have the power to make changes to the budget. It can only make recommendations to the Lok Sabha.
The Lok Sabha can either accept or reject the recommendations within 14 days. Once the Parliament passes the budget, it goes to the President of India for assent. After the President’s nod, the budget is finalized and published in the Gazette of India. The entire process is completed during the budget session of Parliament.








