Maintaining financial stability requires understanding what factors contribute to a good credit score. The higher your score, the more creditworthy you appear to lenders in India, where credit ratings typically range from 300 to 900. Additionally, a good score may lead to quicker loan approvals, higher loan amounts, and better interest rates.
As a result, prudent credit management, whether applied when applying for loans or credit cards, can have a significant impact. Thus, monitoring your credit score contributes to a more seamless borrowing experience.
What is a Credit Score, and How Does it Work?
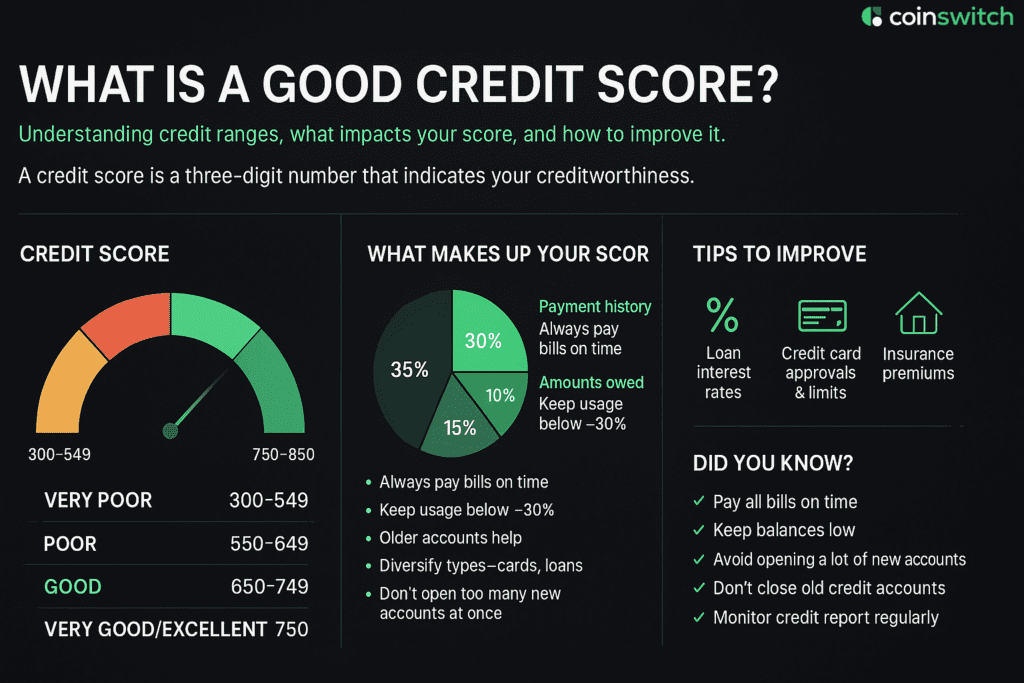
A credit score is a three-digit number that shows lenders your creditworthiness. This 300–900 score in India is based on credit history, repayment habits, outstanding amounts, and credit utilization percentage. To create your credit report and score, credit information agencies use data from NBFCs and banks.
Lenders use these variables to determine your likelihood of making responsible loan repayments. Therefore, having the best credit score makes it possible to obtain favorable terms on credit cards and loans.
How Does a Credit Score Work?
First, credit bureaus gather information on your credit cards, loans, bill payments, and defaults. They also assess variables such as new inquiries, credit utilization, credit type mix, and on-time payments. This data is then combined to create your credit report, which is then converted into a score that ranges from 300 to 900.
In general, your perceived risk decreases with a higher score. Lenders use this score as a quick way to assess your eligibility and the appropriate interest rate. Hence, over time, consistent and prudent credit conduct can raise your credit score.
Read More: Understanding the Cashflow Quadrant: A Pathway to Financial Freedom
What do Different Credit Score Ranges Signify?
Depending on the scoring mechanism, credit score ranges differ. If you have a good score, potential lenders and creditors may be more confident in your loan request since it shows responsible credit behavior. Typically, credit score ranges are as follows:
· 800–850: This group is considered low-risk borrowers. Compared to consumers with lower scores, they may find it easier to obtain a loan.
· 740–799: Since they have a track record of good credit conduct, individuals in this category could find it simpler to get credit.
· 670–739: Generally speaking, lenders consider consumers with credit scores of 670 and above to be acceptable or lower-risk.
· 580–669: People in this group are often referred to as subprime borrowers. Lenders may view individuals as higher-risk, and they may have difficulty obtaining new loans.
· 300–579: People in this category often struggle to obtain new credit. Before you can get any new credit, you’ll probably need to take steps to improve your credit rating if you fall into the low range.
Importance of Credit Score
Above all, your credit score is a trustworthy representation of your level of financial responsibility. As a result, it directly impacts how lenders weigh your reliability. Additionally, a good credit score makes it possible to obtain cheaper interest rates, quicker approvals, and larger loan amounts.
It may also unlock premium credit cards and increase your bargaining power for credit-related items. Additionally, it facilitates seamless financial transactions and minimizes friction when applying for a loan. For this reason, maintaining the best credit score is essential to long-term financial flexibility and stability.
Read More: AMC SIP in Mutual Funds: Meaning and Key Differences from Regular SIP
How to Calculate Credit Score?
Credit bureaus use proprietary formulas to determine your credit score, but you cannot do it yourself. They start by compiling your credit duration, credit mix, usage ratio, credit repayment history, and inquiry volume. Each component is then given a score and weight.
Ultimately, a three-digit credit score ranging from 300 to 900 is created by adding together the weighted values. Therefore, by continuing to make on-time payments, reducing usage, and avoiding frequent new credit applications, you may have a favorable impact on it even if you can’t calculate it directly.
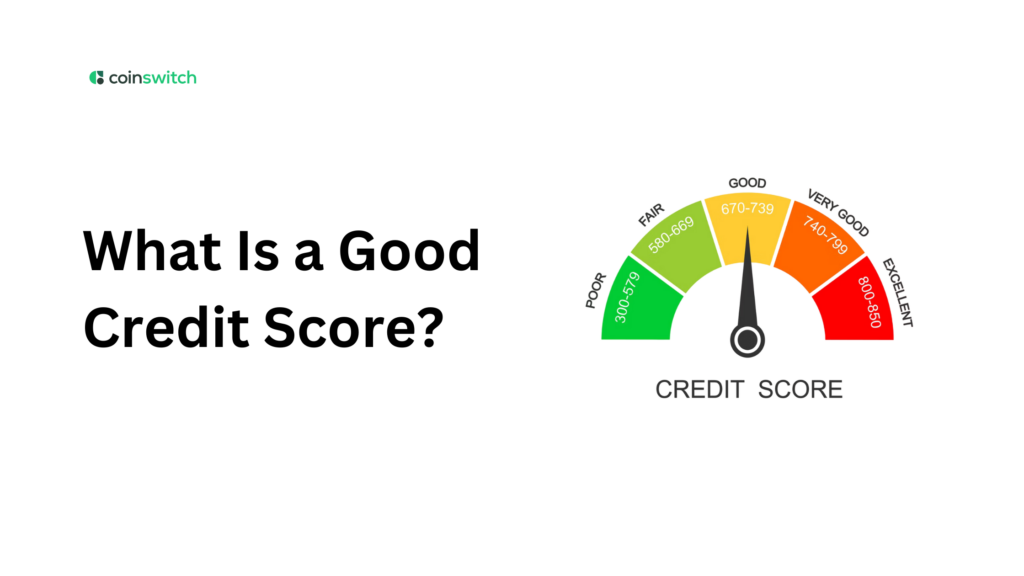
What is a Good Credit Score in India?
A credit score of 750 or higher is generally regarded as outstanding in India, offering favorable terms and a high likelihood of loan acceptance. A good score falls between 700 and 749, and they also have a high chance of being approved.
Fair scores range from 650 to 699, which might lead to restricted approvals and higher interest rates. Approval becomes difficult and expensive below 650, particularly between 300 and 649, which is considered bad.
Why should I check my credit score?
Keep your credit score up to date. Catch errors or fraud at the earliest with RBI-approved bureaus that give one free report every year. Staying current helps you correct and enhance your credit promptly, which is particularly helpful when applying for loans or credit cards.
Reasons for a Low Credit Score
Several common issues can lead to a low credit score.
· Late or missed payments: Reflect poorly on your payment discipline, which harms your score.
· High credit utilization: Your score falls when you use more than 30% of your credit line, which indicates over-reliance.
· Frequent hard inquiries: Applying for many credit cards or loans within a short time indicates heavy reliance on credit.
· Closing old accounts: Shortens your credit history, which is a component in lowering your credit score.
· Limited credit mix: The scoring potential is less if you have only one credit type, e.g., credit cards.
· Credit report errors: Errors in reporting, outdated information, or incorrect balances may reduce your score unfairly.
How to Increase Credit Score Quickly?
To improve your credit score fast, pay due EMIs and payments punctually. Then, pay off your credit card debt until your credit card balance is reduced below 30%. Also, wait until your credit score improves before applying for new credit cards or loans. Maintain the age of your credit history by keeping your old accounts active.
Keep your report updated and dispute any errors as soon as you become aware of them. To build on a good score, have a small personal loan or a secured credit card. In a matter of months, these targeted efforts could result in significant gains.
How does Credit Score Impact Eligibility for Loans and Credit Cards?
Your credit score directly influences your credit and loan approval. First, lenders will judge the risk of repayment against it; the higher the score, the less risky. Hence, high scorers (750+) receive faster approvals and lower interest rates. Second, good scorers (700–749) have good prospects but may face less favorable terms.
On the other hand, fair scores (650–699) can result in tougher scrutiny and increased borrowing costs. Moreover, poor scores (below 650) can lead to outright rejections or limited access to credit. Therefore, the best credit score unlocks more credit options for you.
List of Credit Information Bureaus in India
India has four RBI-authorized credit information companies (bureaus): Experian, TransUnion CIBIL, Equifax, and CRIF High Mark. The first and the oldest credit bureau is CIBIL or TransUnion CIBIL. Experian and Equifax set up their operations in the Indian market in 2010.
CRIF High Mark has been operational since 2010 and is well established in the microfinance and retail industries. All are regulated by the Credit Information Companies (Regulation) Act, 2005, and provide credit score and report facilities. Hence, consumers have the right to obtain one free report per year from each bureau.
What is a Credit Report?
A credit report contains the entire credit history. It has personal details, account type, loan amount, repayment pattern, defaults, credit usage, and enquiry history. Credit bureaus make this report based on data from member banks and NBFCs, which is updated from time to time.
Lenders review your credit history over time. The best credit score provides a snapshot, while the credit report provides complete context. It’s thus essential to check for accuracy and know how your money habits affect your credit record.
Use of Credit Reports
Credit reports perform several essential functions. Banks and NBFCs assess your creditworthiness before approving loans or cards. Employers and landlords can review them, with permission, to determine reliability.
Furthermore, they guide you to improve your credit behavior by highlighting areas such as high utilization or late payments. Hence, credit reports play a crucial role in making informed financial decisions and maintaining a good credit history.
Difference between a Credit Score, Credit Rating, and a Credit Report
A three-digit credit score indicates an individual’s creditworthiness and debt repayment ability. A credit report shows your loans, queries, and payments. Businesses, organizations, and financial institutions use credit ratings to determine a person’s capacity to repay loans.
Individuals rely on good scores and reports for personal finance needs, while organizations depend on ratings to assess corporate credibility. Understanding these distinctions ensures you use each tool accurately.
Why Credit Reports are Important for Businesses?
Businesses use credit reports to assess potential borrowers’ repayment ability and financial discipline. Minimizing lending risks, ensuring informed decisions, and supporting healthy cash flows are their priorities. Strong credit reports enhance MSMEs’ chances of securing loans, trade credit, or supplier contracts, fostering trust and financial stability in commercial ecosystems.
Key Details Included in Credit Report
A credit report includes personal information, details about loans and credit cards, repayment history, outstanding balances, and credit utilization. It records defaults, delinquencies, and inquiries. These insights form a comprehensive picture of an individual’s borrowing behavior and financial reliability for lenders.
Understanding Credit Reports Through Key Terms
Key terms are Credit Utilization Ratio (the share of used credit), Delinquency (missed payments), Hard Inquiries (lender checks that lower the score), Soft Inquiries (self-checks that have no impact), Defaults, and Settlements. These indicators highlight financial discipline, repayment risks, and overall credit health, allowing for better interpretation of your credit report.
Improving your credit health
To improve credit health, pay bills and EMIs on time, keep utilization below 30%, and maintain a balanced credit mix. Limit loan applications, maintain old accounts, and review reports consistently. Correcting errors and building a positive repayment record strengthen creditworthiness and open access to better borrowing opportunities.
Conclusion
The best credit score unlocks financial opportunities. A strong score and a positive credit report lead to easier approvals and better terms. Practice disciplined repayment habits, maintain low utilization, and monitor reports regularly to safeguard your financial credibility. Credit awareness empowers individuals to make better borrowing choices and achieve long-term stability.
FAQs
1. Is 750 a good CIBIL score?
Yes, 750 ranks as excellent in India. This score increases your chances of securing loans and credit cards with favorable interest rates and terms.
2. What’s a good credit score for my age?
Credit scores do not depend on age. A good score typically exceeds 700, and anyone can achieve it at any age by maintaining a disciplined repayment history and using credit facilities responsibly.
3. How to get a 900 CIBIL score?
Achieving 900 is rare, yet it is attainable through excellent habits. Pay bills on time, keep utilization low, maintain long-standing accounts, and avoid frequent loan or credit card applications.
4. Is 800 a good CIBIL score?
Absolutely, 800 stands out as an excellent score in India. Strong repayment behavior reflects minimal risk for lenders and often ensures quick approvals with the best available loan or credit terms.